
Becoming a cybersecurity professional typically involves a combination of education, training, and practical experience. Here’s a general roadmap:
Becoming a cybersecurity engineer involves a combination of education, technical skills, hands-on experience, certifications, and a commitment to continuous learning. Here’s a roadmap to guide you:
- Educational Background:
- Obtain a bachelor’s degree in computer science, information technology, cybersecurity, or a related field. A higher degree or specialized training can also be beneficial.
- Learn Fundamentals:
- Understand the basics of computer networks, operating systems, and programming languages such as Python or PowerShell.
- Familiarize yourself with cybersecurity concepts, including threat modeling, risk assessment, cryptography, access control, and incident response.
- Gain Technical Skills:
- Develop proficiency in using cybersecurity tools and technologies such as firewalls, intrusion detection/prevention systems (IDS/IPS), antivirus software, SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) systems, and penetration testing tools.
- Learn about common vulnerabilities and attack techniques, such as malware, phishing, SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and denial-of-service (DoS) attacks.
- Hands-on Experience:
- Gain practical experience through internships, cybersecurity projects, or entry-level positions in IT or cybersecurity roles.
- Participate in capture the flag (CTF) competitions, cybersecurity challenges, and bug bounty programs to apply your skills in real-world scenarios.
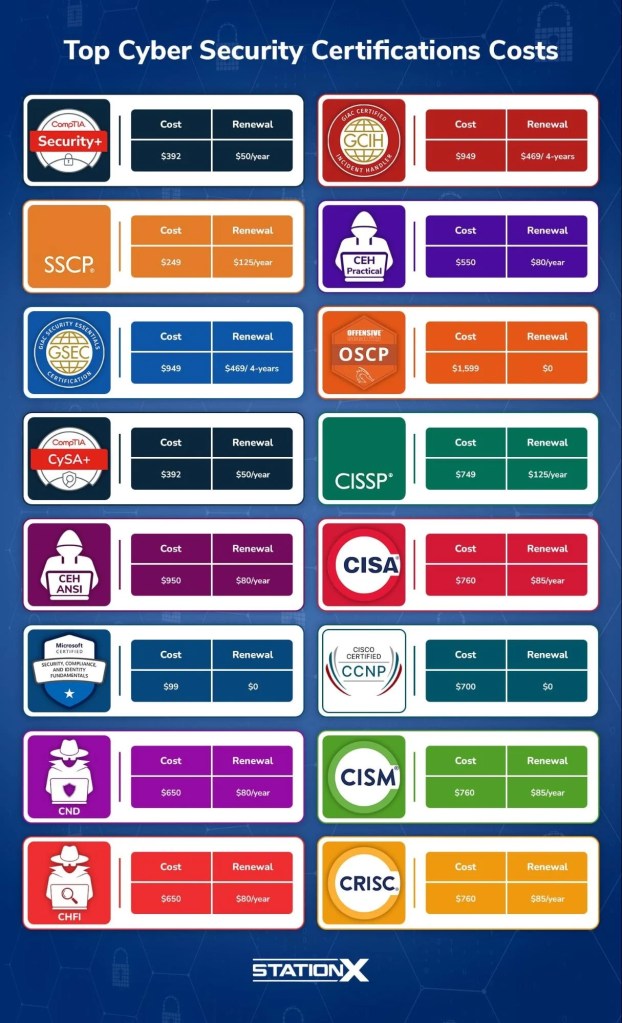
- Certifications:
- Obtain relevant certifications to validate your skills and knowledge. Some recommended certifications for cybersecurity engineers include:
- CompTIA Security+
- Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP)
- Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH)
- Offensive Security Certified Professional (OSCP)
- CompTIA Cybersecurity Analyst (CySA+)
- Certified Information Security Manager (CISM)
- Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA)
- Specialize:
- Consider specializing in specific areas of cybersecurity such as network security, cloud security, application security, incident response, or digital forensics.
- Stay updated with the latest threats, vulnerabilities, and countermeasures in your chosen specialization.
- Soft Skills:
- Develop strong analytical, problem-solving, and critical thinking skills.
- Effective communication and teamwork are crucial for collaborating with colleagues, conveying security concepts to non-technical stakeholders, and presenting findings to management.
- Networking:
- Engage with the cybersecurity community by attending conferences, joining professional organizations (e.g., ISC², ISACA, OWASP), and participating in online forums and communities.
- Networking can provide valuable opportunities for learning, mentorship, and career advancement.
- Ethical Conduct:
- Uphold ethical standards and adhere to legal and regulatory requirements in your work as a cybersecurity professional.
- Commit to continuous learning and ethical conduct to maintain the trust and integrity of the cybersecurity profession.
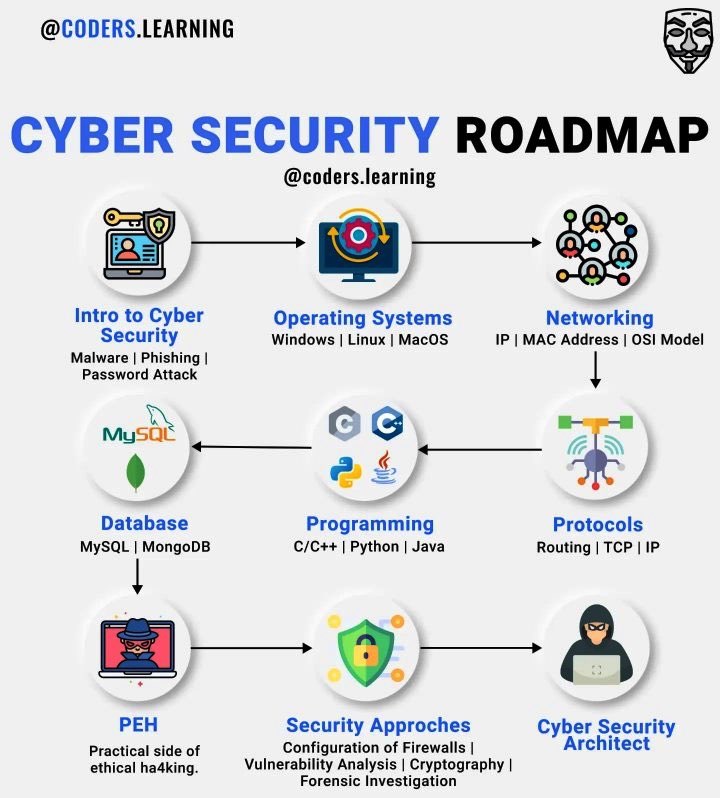
By following this roadmap and continuously improving your skills and knowledge, you can become a successful cybersecurity engineer. Remember to stay curious, keep learning, and adapt to the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity threats and technologies.

Remember, cybersecurity is a constantly evolving field, so adaptability and a willingness to learn are essential qualities.




Leave a comment