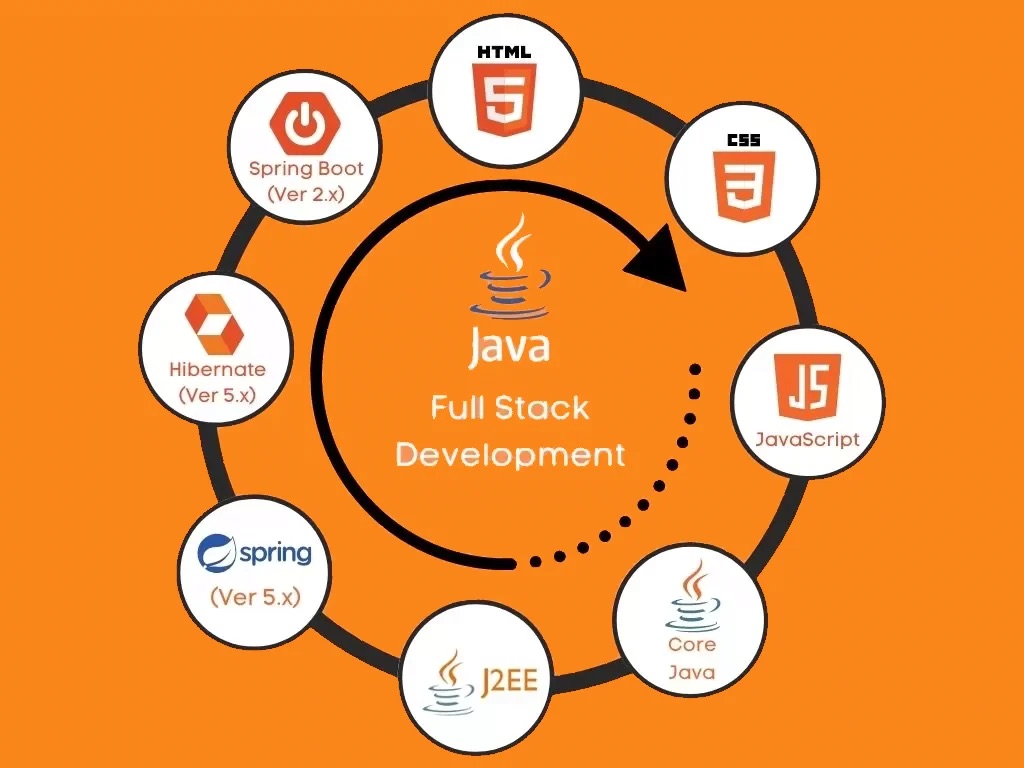
Becoming a full-stack Java developer involves learning both front-end and back-end development using Java technologies. Here’s a roadmap to help you get started:

- Learn Java: Start by mastering the Java programming language, including its syntax, object-oriented principles, and common libraries. There are many online tutorials, courses, and books available to help you learn Java.
- Front-end Development: Familiarize yourself with front-end technologies such as HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. Learn popular front-end frameworks like Angular, React, or Vue.js, which are commonly used in conjunction with Java for building user interfaces.
- Back-end Development with Java: Learn back-end development using Java frameworks and libraries such as Spring Boot, Jakarta EE (formerly Java EE), or Play Framework. These frameworks provide tools and components for building robust, scalable, and secure web applications.
- Database Management: Gain proficiency in working with databases, especially relational databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, or Oracle. Learn how to interact with databases using Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) and Object-Relational Mapping (ORM) frameworks like Hibernate.
- RESTful APIs: Understand how to design and implement RESTful APIs using Java frameworks like Spring MVC or JAX-RS. Learn about HTTP methods, request/response formats, authentication, and authorization mechanisms.
- Version Control: Familiarize yourself with version control systems like Git, which are essential for collaborating with other developers and managing project codebases.
- Build Tools and Dependency Management: Learn how to use build automation tools like Maven or Gradle to manage dependencies, compile code, run tests, and package applications for deployment.
- Testing: Gain proficiency in writing unit tests, integration tests, and end-to-end tests for your Java applications. Learn testing frameworks like JUnit, Mockito, and Selenium.
- Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD): Understand the principles of CI/CD pipelines and how to automate the build, test, and deployment processes using tools like Jenkins, Travis CI, or GitLab CI.
- Deploying and Hosting Applications: Learn how to deploy your Java applications to production environments, whether it’s on-premises servers or cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud Platform.
- Keep Learning and Practicing: The field of software development is constantly evolving, so continue learning new technologies, tools, and best practices. Build projects, contribute to open-source projects, and participate in online communities to hone your skills.
By following this roadmap and continuously learning and practicing, you can become a proficient full-stack Java developer.




Leave a comment