Becoming a data scientist involves acquiring a blend of technical skills, domain knowledge, and practical experience. Here’s a structured guide to help you on this path:
1. Educational Background
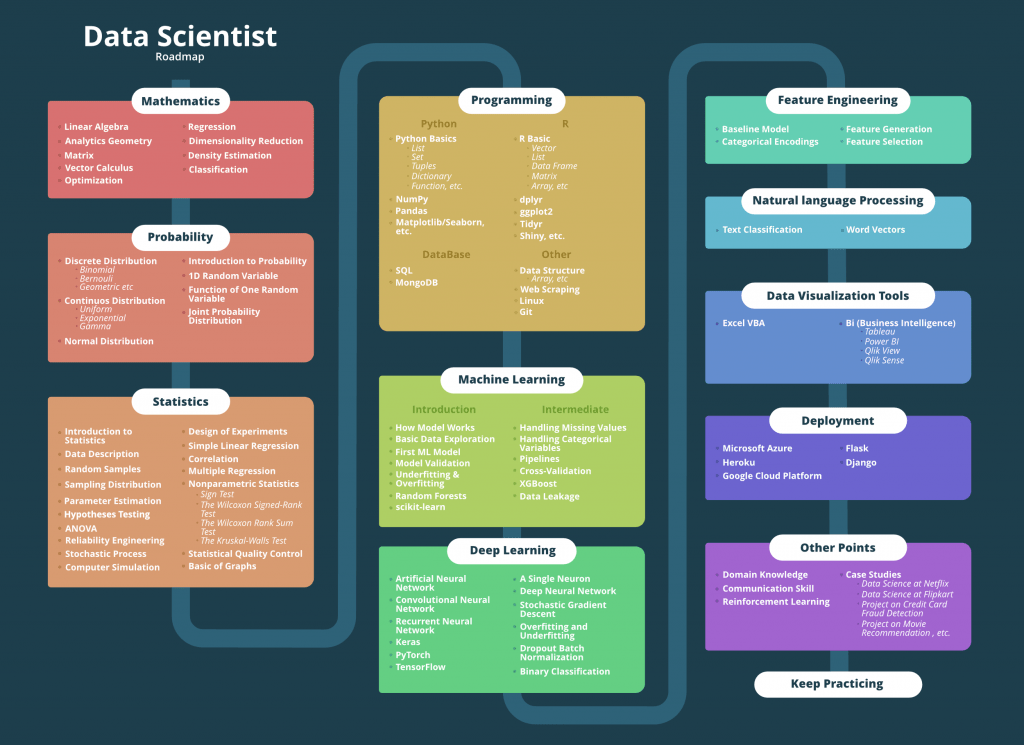
- Formal Education: Pursue a bachelor’s degree in a relevant field such as computer science, statistics, mathematics, engineering, or data science. Some data scientists also have degrees in economics or physics.
- Advanced Degrees (Optional): Consider obtaining a master’s or Ph.D. in data science, statistics, computer science, or a related field for more specialized knowledge and better job prospects.
2. Technical Skills Development
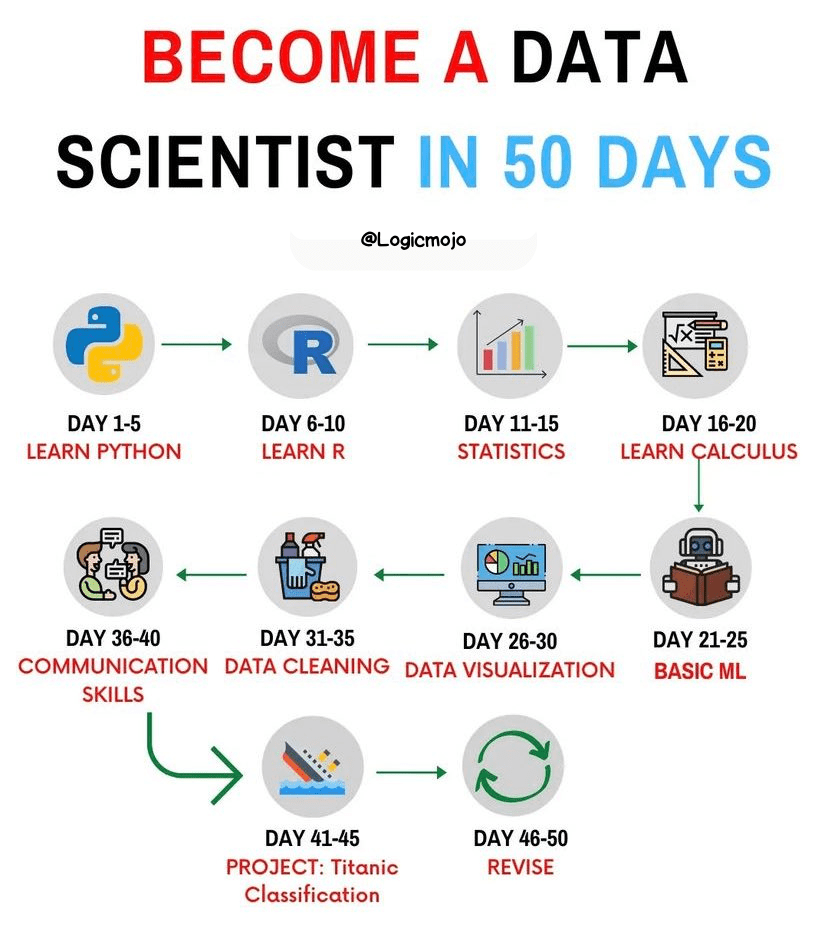
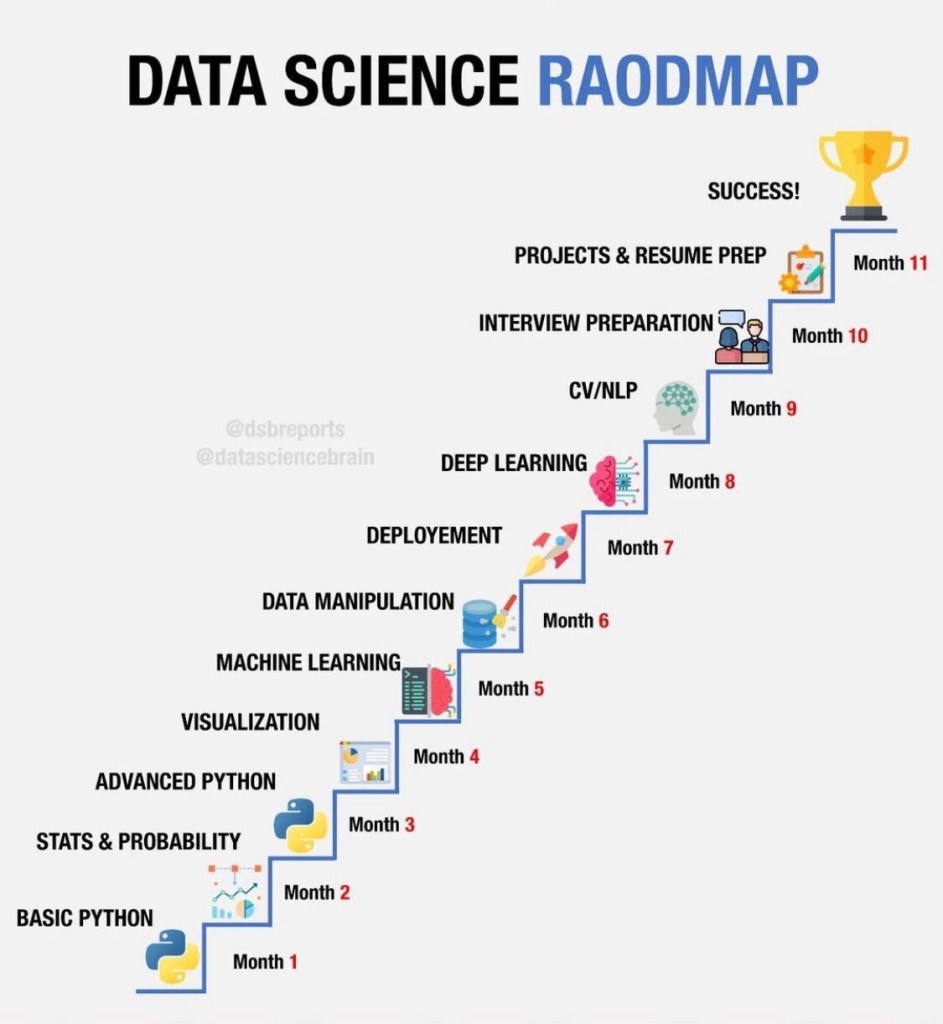
- Programming Languages: Learn Python and R, the two most commonly used programming languages in data science.
- Statistical Knowledge: Develop a strong understanding of statistics and probability.
- Data Manipulation and Analysis: Gain proficiency in using libraries such as Pandas and NumPy in Python, and dplyr and ggplot2 in R.
- Machine Learning: Study algorithms and techniques, and get hands-on experience with libraries like scikit-learn, TensorFlow, and Keras.
- Database Management: Learn SQL to extract and manipulate data from relational databases.
- Big Data Technologies: Familiarize yourself with tools like Hadoop, Spark, and Hive for handling large datasets.
3. Soft Skills
- Problem-Solving: Develop a structured approach to solving complex problems.
- Communication: Enhance your ability to explain technical results to non-technical stakeholders.
- Domain Knowledge: Understand the industry you are working in (e.g., finance, healthcare, marketing) to apply data science effectively.
4. Practical Experience
- Projects: Work on real-world data science projects. Start with small datasets and gradually move to more complex ones.
- Internships: Gain practical experience through internships or part-time roles.
- Competitions: Participate in data science competitions on platforms like Kaggle to practice and showcase your skills.
5. Tools and Software
- Data Visualization: Learn tools like Tableau, Power BI, and matplotlib for creating visualizations.
- Version Control: Use Git for version control and collaboration on projects.
- Cloud Platforms: Get acquainted with cloud services such as AWS, Google Cloud, or Azure, as many data science workflows are moving to the cloud.
6. Continuous Learning
- Online Courses: Enroll in online courses and specializations from platforms like Coursera, edX, Udacity, and DataCamp.
- Books: Read foundational books like “Python for Data Analysis” by Wes McKinney, “Introduction to Statistical Learning” by Gareth James, Daniela Witten, Trevor Hastie, and Robert Tibshirani, and “Deep Learning” by Ian Goodfellow, Yoshua Bengio, and Aaron Courville.
- Conferences and Meetups: Attend industry conferences, workshops, and local meetups to network with professionals and stay updated on the latest trends.
7. Building a Portfolio
- GitHub Repository: Create a public GitHub repository to showcase your projects and code.
- Blogging: Write articles or blog posts to explain your projects and share insights on data science topics.
- LinkedIn Profile: Maintain an updated LinkedIn profile highlighting your skills, projects, and experience.
8. Job Search and Career Development
- Job Boards: Look for data science job openings on job boards like Indeed, Glassdoor, and LinkedIn.
- Networking: Connect with professionals in the field through LinkedIn, meetups, and conferences.
- Interview Preparation: Practice coding and problem-solving for technical interviews. Be prepared to discuss your projects and experience in detail.
Conclusion
Becoming a data scientist requires a commitment to continuous learning and development. By following this structured approach, you can build the necessary skills, gain practical experience, and successfully transition into a data science career.




Leave a comment